Unless you’ve been living under a rock, you already know there are currently hundreds of thousands of cases of Covid-19 worldwide. But that’s not all.
In 2017, thousands of people in the United States alone died from the flu.
In 2003, over 8,000 people became ill with symptoms of SARS, and of these, over 700 died.
Needless to say, infectious diseases need to be taken seriously.
So how do we stop the rapid spread and stay safe from infectious diseases? Now more than ever, it’s vital to know and understand the modes of transmission of infectious diseases in order to control and eventually stop them.
Avoiding direct contact is only one of the ways that you can avoid transmission. There are nine ways that you could catch an infectious disease. By understanding how infectious diseases are transmitted, you stand a better chance of protecting yourself and your loved ones.
| Related: Sterilis Wins “Technology for a Better Tomorrow” Leadership Award from MassTLC |
Table of contents
Reservoirs
What is a reservoir of infection?
A reservoir is a place in which a pathogen lives and in which the infection caused can be transmitted to the target population.
Reservoir of infection examples
There are three types of reservoirs in which a pathogen can live.
- An animal
- A human
- Environment
Human Reservoir
Some pathogens can be transmitted from human to human. Some diseases can be transmitted strictly by touch, while others, like sexually transmitted infections (STIs), are transmitted through the exchange of bodily liquids.
Some humans may be carriers of infection.
This means that they can have the infection without experiencing the side effects, but they can still transmit it to another person. Many carriers will never realize that they have a disease and thus will take no precautions against transmission.
Learn more about how to dispose of medical waste from Sterilis Solutions to avoid transmission of infectious diseases
Animal Reservoir
Humans can also get diseases that derive from animal reservoirs.
This can happen by eating meat, and in some cases, by touching or being bitten by an infected animal. Many newly recognized infectious diseases such as SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome), HIV/AIDS, and Ebola are thought to have originated from animals.
When discussing animal reservoirs, you might hear the word zoonosis.
Zoonosis refers to an infectious disease that can be transferred from animals to humans. It’s important to recognize that just because a disease is zoonotic, that does not mean that it can be transferred from human to human (contagious), which is when things really become a big problem.
Environmental Reservoir
Plants, Soil, and Water in the environment can also serve as reservoirs for infectious agents and pathogens. Environmental Reservoirs include both lying and non-living reservoirs. Specific agents like fungal agents live and multiply in soil. This can be incredibly dangerous.
Modes of Transmission of Infectious Diseases

Diseases can spread through either direct or indirect contact. In this section, we’ll explore the specifics of these contact occurrences.
Infectious Disease Transmission Through Direct Contact
The first way that infection can spread is through direct contact. There are four main ways that direct contact occurs. Let’s dive in.
Person to Person Contact
Infectious diseases can be transmitted from person to person through touch. This includes giving a kiss or a hug, a handshake or a high five, or even just a brush up against someone in a grocery store.
To prevent the spread of person to person contact, be sure to frequently wash your hands and avoid touching people who are not in your family unit. Medical waste should always be properly disposed of to prevent any accidental person to person contact.
Maintaining proper social distancing is key to preventing direct contact. If you are unfamiliar with the practice, the purpose is to increase the space between yourself and others, thereby decreasing the frequency of contact and decreasing the likelihood that an infectious disease can be transmitted to you or others. In our current situation, many businesses are taking the practice of social distancing and putting it into significant effect in the workplace by distancing coworkers and clients and customers from one another. Social distancing can also help with other modes of transmission listed below.
Related: Bloomberg Article – This Needle Grinder Can Mash Up Medical Waste in an Hour
Droplet Spread
Some infections can be spread via droplet spread, which is where airborne particles that contain the infection (from a cough, sneeze, or a bit of spit while talking) land on another person or object and are then transmitted into the body.
This transmission can happen through the scratching of the face, and the particles enter the body through the mouth, nose, or eyes.
Mother to Unborn Child
Some diseases are transmitted from a pregnant mother to an unborn child. Diseases like syphilis or chickenpox can infect the mother while pregnant, and when the child is born, they may also have this disease.
To prevent the child from having the disease, the mother needs to take precautions to stay away from the disease while pregnant. This can be incredibly difficult around people who are unaware of the risk to pregnant mothers. Educating those around you about these dangers can help provide for a safer environment for our mothers-to-be.
Need help disposing medical waste properly? Check out Sterilis Solutions for more information
Animal to Person
As we know from learning about animal reservoirs, animals can also transmit diseases to humans.
This can happen by an animal bite or by consumption of animal flesh or byproduct. Certain diseases can survive in animals as well as in their environment without infecting them. Of course, you should be wary of direct transmission from animal to human, but it is also important to note that being in their habitat puts you at risk for infection. You don’t necessarily have to be bitten or even touched by a sick animal. Not all diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans can be transmitted from humans to humans.
If it’s possible that an animal has an infection, it’s vital that humans, especially old, young, and autoimmune humans, stay away from the animal until it can be tested and declared safe.
Indirect Contact
Next, diseases can spread through indirect contact, which occurs in four main ways.
Contaminated Objects
Contaminated objects can transmit infectious diseases. For example, someone who has the infection (either knowingly or unknowingly as a carrier) touches a milk carton in the store and leaves the virus there.
You pick up the same carton, and the virus is now on your hands. As soon as you touch your nose, mouth, or eyes, the virus is inside your body and begins infecting you.
Everything from shopping carts, phones, computers, subway handles, and more are sites for infection. The easiest way to combat contaminated objects is to keep hand sanitizer as well as sanitizing wipes handy. Regularly sanitize items that you carry with you every day like your water bottle, backpack, keys, etc.
Airborne Transmission
Airborne transmission refers to diseases that can remain in the air (like oxygen and water remain in the air), and that can survive for long enough periods of time that they can find a new host. Airborne particles are then inhaled by a new host who will then either become sick and show symptoms or become a carrier of the disease.
Animal Reservoirs
Animals can also transmit diseases via indirect contact. Just like humans, if an animal is infected and they contaminate an object or if the disease is airborne, another animal or a human could become the new host of the disease.
If a diseased animal is slaughtered and turned into meat for human or animal consumption, the meat could act as a contaminated object.
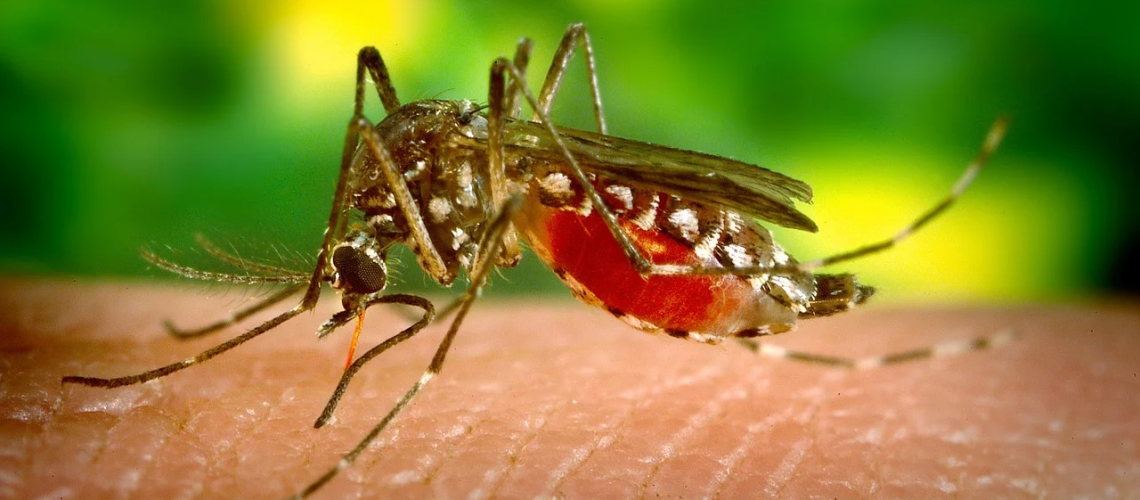
Insect Bite (Vector-Borne Disease)
Vectors are animals or insects that can transmit disease.
Mosquitos are quite a common vector because as they draw blood from their prey, they release some of their infected saliva. Vectors can also spread diseases through their feces or simply by physical contact with a new host.
Dispose of medical waste properly with Sterilis Solutions to avoid transmission of infectious diseases to healthcare workers and patients
How to Prevent Disease Transmission

The best way to prevent disease transmission is to first understand what the disease is and the modes of transmission of infectious disease. Once you know what the disease is and how it’s transmitted, you’ll have a better idea of how you can prevent catching it and spreading it.
If it’s spread by contact or droplets, constant hand and clothing washing and staying at least 6 feet away from others is the best thing that you can do. If it’s airborne, staying away from others whenever possible is the best solution. If it’s spread by animals, stay away from animals and meat that you’re uncertain of can help prevent infection and spread.
You should invest in your supply of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Ensure that you have gloves, masks, sanitizer, bug spray, etc. These items can be the difference between getting infected and staying healthy. It is incredibly important to know the different PPE types available to you and use the right PPE for the problem.
As always, you should keep maintaining good hygiene as a priority. If you are not washing your hands regularly after touching foreign objects, you open the door to the possibility of infection. Remember to clean with hot water and adequately scrub your hands even up to your wrists. Cover your mouth if you have to sneeze or cough. Make sure you have no open wounds or cuts that could be open to airborne infection.
Remember food safety protocols. For example, do not cut raw chicken with a knife and use the same knife to prep your veggies. Also, remember to cook your food thoroughly. A food thermometer should be a go-to daily tool for your kitchen!
Suppose you intend to go out and put yourself at risk. Make sure that you are up to date on all your vaccines! If you are traveling, take the necessary precautions to ensure your health and safety while abroad.
Remember, you are responsible for your health. Keep yourself clean and healthy. If you have any questions, reach out to your doctor. Get tested regularly, and finally, taking control of medical waste is absolutely vital.
Medical waste should be properly and quickly disposed of to prevent further spread of infection.
Related: New technology helps clean up areas littered with heroin needles
- How to Return to Work Safely
 As the year 2020 marched forward, it became evident that COVID-19 would force a lockdown across the U.S., if not across the globe. For seemingly endless months, everyone has had ... Read more
As the year 2020 marched forward, it became evident that COVID-19 would force a lockdown across the U.S., if not across the globe. For seemingly endless months, everyone has had ... Read more - Steps to Take Following a Needlestick
 It’s not difficult to believe that the healthcare industry is a hazardous industry to work in. Even as the current pandemic has relegated most of the country to their homes, ... Read more
It’s not difficult to believe that the healthcare industry is a hazardous industry to work in. Even as the current pandemic has relegated most of the country to their homes, ... Read more - What Are Some Examples of Biohazard Waste?
 Table of Contents What are some examples of Biohazard Waste? What is Biohazardous Medical Waste? Primary Categories of Medical Biohazard Waste Disposal of Common Biohazardous Waste If the term “biohazardous ... Read more
Table of Contents What are some examples of Biohazard Waste? What is Biohazardous Medical Waste? Primary Categories of Medical Biohazard Waste Disposal of Common Biohazardous Waste If the term “biohazardous ... Read more
