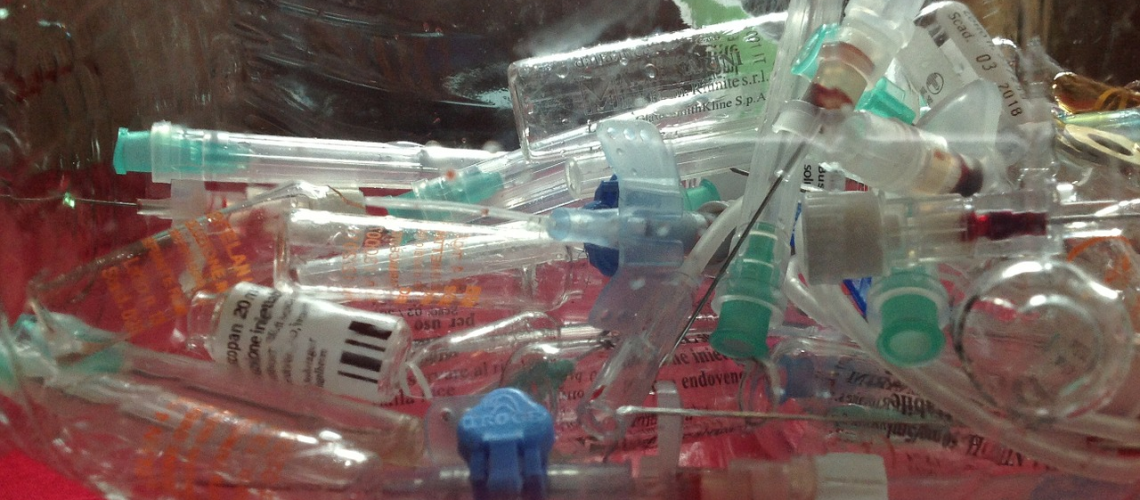
Hospitals in the United States create about 25 pounds of medical waste per patient each day. Strict regulations are made to ensure proper medical waste disposal for safety reasons. Improper disposal puts people at risk of exposure to hazardous or infectious materials.
Unregulated discarding medical waste is a bad practice. Keep reading to learn about why proper disposal is necessary, the risks, the types of waste, removal and control plans everyone in the healthcare industry should know.
Related: How Sterilis Works
Skip to section
Why Focus On Proper Medical Waste Disposal
Environment, Regulations and Public Health
Who is at Risk for Exposure to Medical Waste?
Why Focus On Proper Medical Waste Disposal?
The steps to proper disposal of medical waste are critical to adhere to. Unchecked waste poses a risk not only to human health but is also harmful to the environment.
Federal and state health departments have guidelines for how to remove waste safely. Some of these measures may include sterilization before disposal or incineration.
As mentioned above, federal and state regulations outline how to dispose of specific waste by classification. It is also important to remember that individual states classify particular items in different categories. Always check your state’s specific guidelines for disposal. You run the risk of breaking the law and can be punished for your failure to observe state and federal regulations.
Looking for a safe, simple, and sustainable way to dispose of medical waste? Check out Sterilis Solutions
Environment, Regulations and Public Health
The amount of hazardous and infectious waste from hospitals is around 15% of total waste.
Although, all medical waste, infectious or not, is a potential risk to public safety. It was not until 1988, biomedical waste was only regulated by state agencies.
When infectious waste began to appear in public areas, such as beaches, disposal protocols became more strict. Groups like the EPA, CDC, OSHA, and FDA have protocols in place to lower the risk of exposure.
Guidelines for classifying medical waste are also widely used to regulate proper disposal.
Who is at Risk for Exposure to Medical Waste?
Hospital workers
Hospital workers are at a higher risk of exposure to disease. Sharps, fluids, medication, and other waste pose safety issues if not properly discarded.
Sanitation workers
Sanitation workers are susceptible to needle sticks or contact with infectious waste.
Incorrect disposal of medical waste can be dangerous. Substances can leak into our oceans and pollute our water supplies. Toxic chemicals in water harm the aquatic life and people who come in direct contact with it.
Medical waste is not merely just used needles, sharps, and swabs. Medical waste also includes pharmaceuticals. Waste in this form can be especially dangerous considering the effects. Burns, poison, as well as the environment, can be affected.
Without diving into radioactive waste like the byproduct of chemotherapy treatment, the issue of risk to exposure quickly becomes a pressing societal issue.
If you are exposed to medical waste in any fashion, immediately take the proper steps to ensure your health and wellbeing.
Types of Medical Waste

Medical waste is broken into different categories. Each type needs to be handled and discarded separately. These categories include:
Infectious waste
Solid waste materials can cause human disease and can be suspect of contamination in human pathogenic organisms.
Infectious waste is anything infectious or contaminated. This can be contaminated equipment, clothing, anything removed from a sick patient in surgery.
It also includes materials used for patients with contagious diseases.
It is critical to managing infectious waste properly when storing, treating, transporting, and disposing of because Infectious waste poses a constant threat to humans that come in contact.
Below are different categories that show examples of medical waste.
Pathological waste
A category of biohazardous waste. Not only materials that come from the human body, But also animals. Organs, blood, fluids, and body parts.
Sharps waste
Needles, syringes, scalpels, blades, broken glass, lancets, etc.
Chemical waste
This includes any liquid waste, typically from machines and batteries, as well as laboratory solvents, reagents, disinfectants, and mercury.
Pharmaceutical waste
Medication that is unused, expired, contaminated or otherwise unusable. Such as pills, tablets, chewable, suppositories, creams, ointments, balms, etc.
Cytotoxic waste
Hazardous medical waste products with genotoxic properties. These are usually byproducts of cancer treatments and may be mutagenic or carcinogenic.
Radioactive waste
Products have been contaminated by radioactive materials. These materials are used for medical treatment or diagnostic purposes.
General waste
This is the majority of medical waste, think household and office items. This also includes waste that does not show a direct threat to public or personal health.
Medical waste cannot be thrown away in a normal garbage can. Medical waste must also be separated by type.
Failing to do so endangers everyone who comes in contact with it. Proper disposal is essential to limit the disease-causing potential of medical waste. As mentioned above, separating medical waste by type is paramount. Not all medical waste can be disposed of correspondingly.
Related: Why Sterilis?
How is Medical Waste Disposed of?
Medical waste should be separated and properly marked for disposal. It must be treated according to state and/or federal protocols. The process for disposing of sharps or infectious waste is different from general waste. Medical waste could have harmful consequences if someone is exposed. Therefore, it’s important to follow the medical waste disposal methods according to state or federal protocols.
What is the safest way to dispose medical waste?
Medical waste is often sorted in different colored containers for later pick-up and disposal. The most common solution for disposal is incineration.
General medical waste can be disposed of in a landfill like normal waste.
Incineration is effective for destroying hazardous or infectious medical waste. It also reduces the volume of the waste.
However, this method releases toxic pollutants into the air. This can inadvertently become harmful to human and environmental health. Improper treatment or burning the wrong waste can be toxic to humans and the environment. Certain types of chemical waste can even release carcinogenic smoke.
The drawbacks of this method make it unsustainable and impractical for the future. New technologies allow medical facilities to take care of medical waste on-site safely.
Check out Sterilis Solutions for a fast and convenient medical disposable solutions
Components of an Exposure Control Plan
An Exposure Control Plan is an essential document for healthcare facilities. It limits employee risk of exposure to infectious fluids, materials or bloodborne pathogens. The standards for this plan are by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). In order to be OSHA compliant, the components of an Exposure Control Plan must be:
- A document written for your specific facility
- Updated annually or when changes in technology occur
- Devices and technology must available to limit employee exposure to potentially infectious materials
- Available for every employee
Employees should be familiar with the steps detailed in the Exposure Control Plan. Sharps containers and other medical waste disposal bins are an important part of an effective exposure control plan.
If an employee is exposed to infectious waste, first aid measures should be taken. The next step is a thorough medical evaluation and testing. The incident should be documented so changes can be made to the current plan.
Methods of Compliance PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)
One part of an effective exposure control plan is personal protective equipment (PPE). It must be readily available in enough amounts and sizes. PPE includes gloves, eye goggles, gowns, aprons, masks, face shields, head and shoe cover, and more.
Employees should know where the PPE is located. Correct handling and use are needed to limit their risk of infection exposure.
An important distinction within PPE is the grade required. For example, there are multiple grades of masks available.
Surgical masks
Surgical masks, commonly known as 3-ply or 4-ply, are designed to prevent splatter from entering your mouth, and they are meant to be used in a sterile environment.
N95 masks
N95 masks are designed for a contaminated environment like a construction site where debris is in the air. These masks each fulfill a different purpose.
Your PPE needs must be appropriately met. A 3-ply surgical mask would not be able to perform correctly in a contaminated environment.
PPE should always be kept in stock. You must stay on top of your PPE supplies, especially given current events. The safety and health of not only yourself but your employees should be the main priority for any business.
Employees should know where the PPE is located. Correct handling and use are needed to limit their risk of infection exposure. PPE’s purpose is broader than limiting infection. It is also your protection for the environment you are required to operate in. Failure to understand the risks associated with improper PPE choice or lack of PPE can be deadly.
Related: Sterilis Practice Types
Training Vaccination
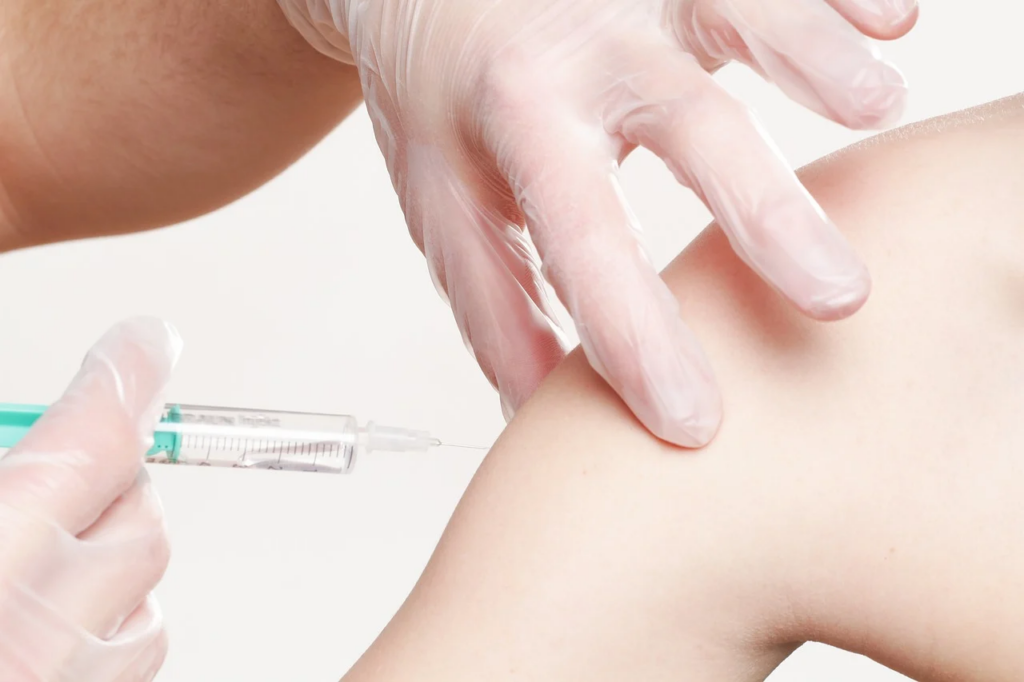
Another crucial element of a proper Exposure Control Plan is providing vaccines to employees. OSHA requires healthcare workers are offered a Hepatitis B vaccine. This is offered for no cost and given within 10 days of the employee’s training. Other professions require specific and unique shots as well. Be sure to stay current with any necessary vaccinations for your position.
This is a safeguard for workers. If they come in contact with Hepatitis B, they are protected. Vaccination is also required post-exposure. Employees may decline the vaccination altogether, but the employee must sign a refusal form.
Remediates medical waste into sterile trash at point-of-care with Sterilis Solutions
Medical Waste Disposal
The process of proper medical waste disposal is an essential step in overall safety. Proper handling of medical waste benefits employees and public safety and improves compliance. Learn more about the best new technology for medical waste technology.
- How to Return to Work Safely
 As the year 2020 marched forward, it became evident that COVID-19 would force a lockdown across the U.S., if not across the globe. For seemingly endless months, everyone has had ... Read more
As the year 2020 marched forward, it became evident that COVID-19 would force a lockdown across the U.S., if not across the globe. For seemingly endless months, everyone has had ... Read more - Steps to Take Following a Needlestick
 It’s not difficult to believe that the healthcare industry is a hazardous industry to work in. Even as the current pandemic has relegated most of the country to their homes, ... Read more
It’s not difficult to believe that the healthcare industry is a hazardous industry to work in. Even as the current pandemic has relegated most of the country to their homes, ... Read more - What Are Some Examples of Biohazard Waste?
 Table of Contents What are some examples of Biohazard Waste? What is Biohazardous Medical Waste? Primary Categories of Medical Biohazard Waste Disposal of Common Biohazardous Waste If the term “biohazardous ... Read more
Table of Contents What are some examples of Biohazard Waste? What is Biohazardous Medical Waste? Primary Categories of Medical Biohazard Waste Disposal of Common Biohazardous Waste If the term “biohazardous ... Read more